7 Poultry Farming Guidelines for Novice Chicken Farmers
Poultry farming can be a rewarding venture when approached with the right knowledge and practices. Here are 7 Poultry Farming Guidelines for Novice Chicken Farmers to ensure a successful and sustainable operation.
1. Selection of Chicks
For a novice chicken farmer, the selection of chicks is the most important part for poultry farming guidelines. Some meat chicken farmers only focus on the price of chicks, overlooking their quality. The quality of chicks is the foundation of successful meat chicken farming. Only by choosing high-quality and healthy chicks can ideal farming results be achieved.
The quality of chicks directly affects the growth of meat chickens and the economic efficiency of the poultry farm. Therefore, it is essential to choose chicks from reputable breeding facilities, rejecting chicks with symptoms of omphalitis and white diarrhea during acquisition. Eliminate weak and deformed chicks, and strictly avoid purchasing low-quality chicks.

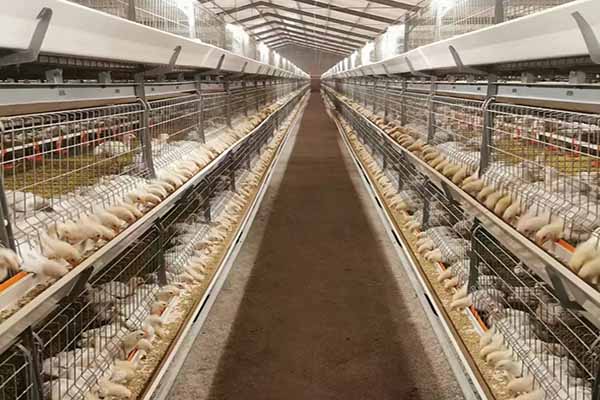
2. Farming Method——Chicken Battery Cage
Currently, many farmers still practice ground-level farming, which makes chickens susceptible to cold and symptoms like diarrhea. This method is unfavorable for controlling intestinal diseases, especially in preventing difficult-to-control diseases like colibacillosis and coccidiosis. It is recommended to adopt chicken battery cage farming for advantages such as saving bedding materials, reducing the occurrence of diseases, and facilitating environmental control. chicken battery cage are particularly suitable for meat chicken farming.

3. Heating Method
Coal heating is a common method in rural chicken farming. However, burning coal consumes a large amount of oxygen inside the house, producing harmful gases such as carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen sulfide, significantly reducing air quality. The issues manifest in several ways:
- Poor coal quality leading to excessive smoke.
- Elevated carbon dioxide levels inside the house.
- Incomplete coal combustion causing carbon monoxide production.
- Excessive oxygen consumption resulting in oxygen deficiency.
It is advisable to use alternatives like heating pads or heating systems to maintain temperature.
4. Ventilation
During the initial stages, attention should not be solely on insulation; ventilation should not be neglected. High temperatures, stale air, and dust in the house can lead to respiratory issues such as tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, and airsacculitis.
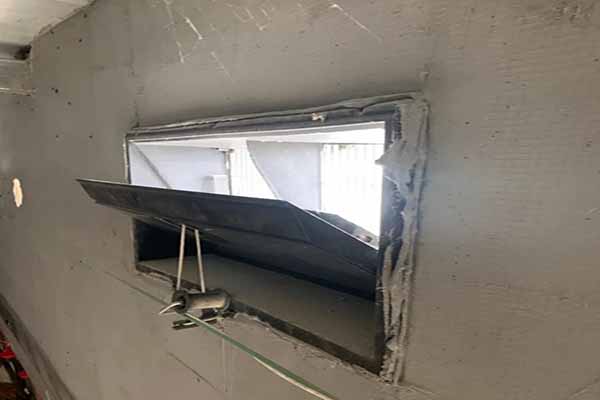
Ventilation design should include skylights positioned approximately 60 cm above the roof ridge to facilitate the expulsion of harmful gases like ammonia and prevent the influx of outside air through the skylights. This creates an effective ventilation route comprising doors, windows, and skylights, promoting the timely removal of stale air.
In later stages, while strengthening ventilation, insulation should not be overlooked, especially during disease outbreaks, changing weather, and seasons with significant day-night temperature differences.

5. Monitoring Temperature and Humidity
High temperatures in brooding rooms often lead to low relative humidity, resulting in dry air, airborne dust, and respiratory issues in chicks. Maintaining humidity between 60-70% is crucial during the brooding period.
Practice has shown that humidity exceeding 80% or falling below 40% adversely affects chicken growth. In cases of low humidity, measures such as floor sprinkling, aerial misting, or adding water pans to the heating system can be employed to increase humidity.
6. Emphasize Chicks Selection and Group Feeding
In poultry farming guidelines, Selecting chicks and group feeding are vital factors in ensuring the health and uniform growth of the chicken flock. The first chick selection should occur upon arrival in the brooding area, isolating weak or small chicks for separate feeding and eliminating deformed chicks to purify the flock.
The second chick selection, at 6-8 days old or during the first vaccination, involves isolating and feeding small-sized or poorly growing chicks separately. Group feeding is recommended as the physiological requirements and responses differ between male and female broilers. Implementing gender-specific group feeding allows for adjusting feed levels more effectively, enhancing feed efficiency.
7. Feed Restriction and Water Control
To prevent rapid growth and associated issues like ascites and sudden death syndrome, feed restriction is advisable before 20 days of age.
In later stages, adding 1-2% garlic to the feed can prevent enteritis and stimulate appetite, potentially reducing the overall rearing period. During disease outbreaks requiring systemic treatment, water control of 0.5-2 hours before medication is recommended. Additionally, during water-immunization, water control of 2-4 hours is suggested, with control duration based on factors such as chicken age, season, growth status, and drug half-life.

Livi Machinery’s Comprehensive Poultry Farming Equipment Supply
For an integrated approach to poultry farming, consider Livi Machinery as your reliable supplier of poultry equipment. With a range of automated solutions, including cage systems and environmental control, Livi Machinery helps save time, energy, and enhances overall efficiency for poultry farmers. Contact us today to embark on your poultry farming journey with professional equipment and dedicated support.
Leave us a message, and our specialized poultry farming team will address all your equipment-related inquiries.